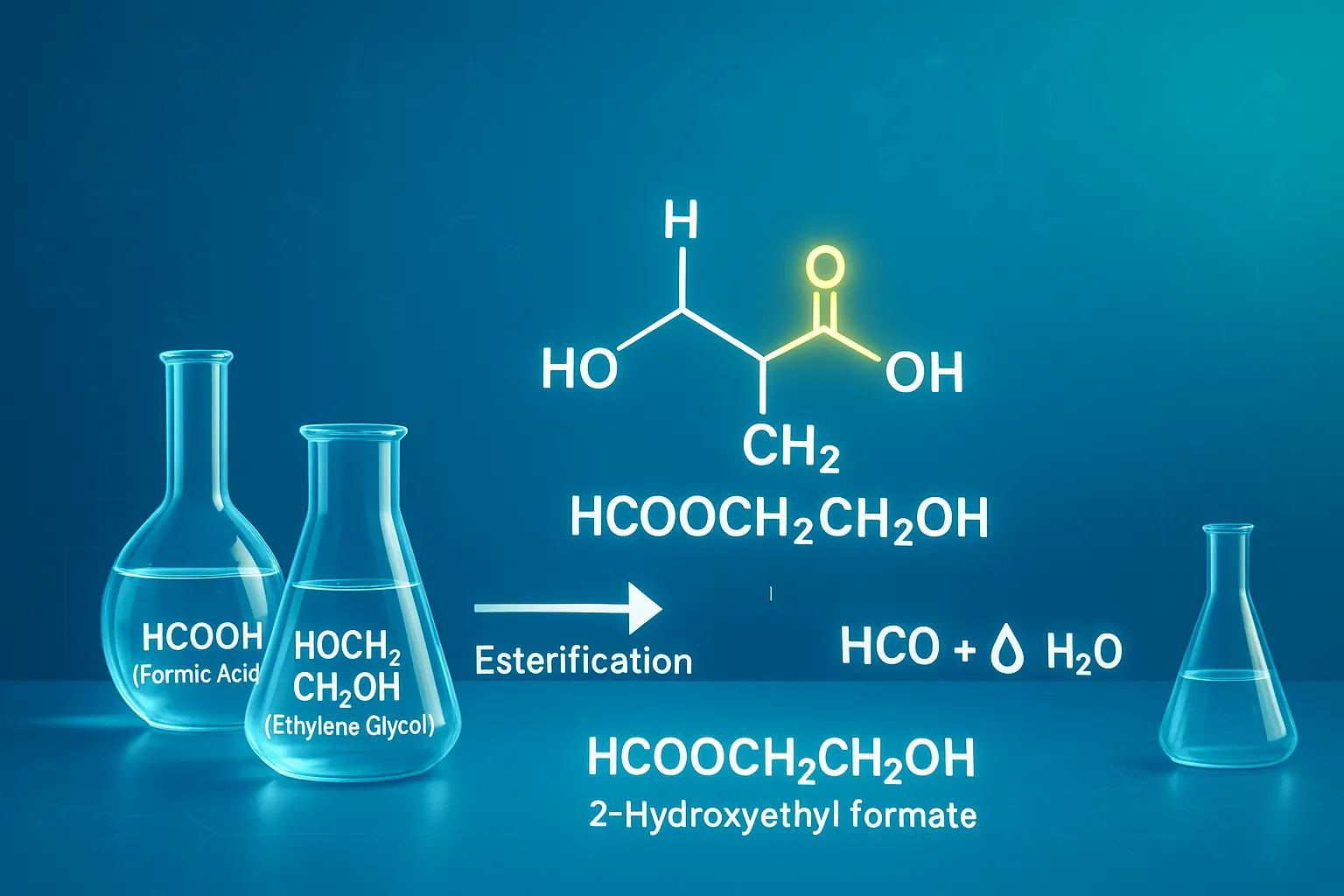
Definition: The chemical compound HCOOCH CH2 H2O, more accurately represented as 2-hydroxyethyl formate (HCOOCH₂CH₂OH), plays a key role in organic and industrial chemistry. This compound is a hydrated ester formed from formic acid and ethylene glycol, and it helps researchers understand esterification and hydrolysis mechanisms that are vital for green chemistry, fuel research, and synthetic processes.
The chemical string “hcooch ch2 h2o” encapsulates a key reaction in organic chemistry: the hydrolysis of an ester known as 2-hydroxyethyl formate (or ethylene glycol monoformate), HCOOCH CH2 H2O. This ester is derived from two common molecules: formic acid and ethylene glycol. Understanding its structure and its interaction with water is essential to appreciating its role in synthetic chemistry and industrial processes.
Decoding the Molecular Structure: HCOOCH CH2 H2O
The compound HCOOCH CH2 H2O is an organic molecule classified as an ester-alcohol. This unique dual functionality gives it distinct properties compared to simple esters or simple alcohols.
- The Formate Group (HCOO): This is the acyl part derived from formic acid (HCOOH), the simplest carboxylic acid.
- The Alkoxy Group (-CH2 CH2 OH): This part is derived from ethylene glycol (HOCH2 CH_2OH), which is a diol (an alcohol with two hydroxyl groups). Since one of the hydroxyl groups reacted to form the ester, the other OH remains free.
Systematic Name: 2-Hydroxyethyl formate.
Common Name: Ethylene glycol monoformate.
Key Feature: The presence of both an ester (-COO-) linkage and a free hydroxyl (OH) group on the same molecule.
Applications of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
🔬 1. Chemical Intermediate
It serves as a precursor for various formate esters used in solvents, coatings, and resin formulations.
⚗️ 2. Green Energy and Hydrogen Storage
Because formates can decompose to release hydrogen gas, this compound is studied as a potential liquid hydrogen carrier in fuel-cell technologies.
🧴 3. Solvent in Laboratory Reactions
It’s used as a mild solvent in esterification, transesterification, and polymerization studies due to its stability and compatibility with aqueous systems.
🌱 4. Eco-friendly Chemical Research
Its low toxicity and biodegradability make it ideal for testing sustainable reaction systems and bio-based materials.
The Central Reaction: Ester Hydrolysis with H2O
The addition of H2O (water) to this ester sets the stage for the reaction known as hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is the chemical decomposition of a substance by reaction with water, and for esters, it specifically breaks the ester (-COO-) linkage.
The Mechanism of Ester Hydrolysis
Ester hydrolysis can occur under either acidic or basic conditions. The overall reaction for the hydrolysis of HCOOCH CH2 H2O is the same, regardless of the catalyst, producing its parent acid and parent alcohol:
HCOOCH CH2 OH + H2O ⇌ HCOOH + HOCH CH2 H2O
- Reactants:
- 2-Hydroxyethyl formate (HCOOCH CH2 H2O): The ester being broken down.
- Water (H2O): The agent that breaks the bond.
- Products:
- Formic Acid (HCOOH): The carboxylic acid component.
- Ethylene Glycol (HOCH2 CH2 H2O): The diol (alcohol) component.
The hydrolysis is an equilibrium reaction, meaning it can proceed in both directions: esterification (acid + alcohol → ester + water) and hydrolysis (ester + water → acid + alcohol).
1. Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
In the presence of a strong acid catalyst (like H2SO4), the reaction rate increases. The acid protonates the carbonyl oxygen, making the ester more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by the water molecule.
2. Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis (Saponification)
Under basic conditions (using NaOH or KOH), the reaction is irreversible and is often called saponification. The hydroxide ion (OH−) acts as a strong nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon. The immediate products are a carboxylate salt (sodium formate) and ethylene glycol.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O+NaOH→HCOO−Na++HOCH2CH2OH
Significance of HCOOH and HOCH2CH2H2O
The products of the hydrolysis—formic acid and ethylene glycol—are themselves important industrial chemicals:
| Product | Formula | Key Uses |
| Formic Acid | HCOOH | Preservative, antibacterial agent, coagulant in rubber production, and a key reagent in chemical synthesis. |
| Ethylene Glycol | HCOOCH CH2 H2O | Used widely as an antifreeze agent, a raw material for polyester fibers and resins (like PET), and as a coolant. |
The hydrolysis reaction is a key method for recovering these valuable components from the ester, making the compound HCOOCH CH2 H2O an important intermediate in certain synthetic routes.
Safety and Handling
While generally considered low-toxicity, HCOOCH CH2 H2O should be handled with care:
- Avoid prolonged skin or eye contact.
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area.
- Use gloves and goggles when performing laboratory experiments.
Always refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for specific safety guidelines.
Summary of “hcooch ch2 h2o” Intent
In summary, HCOOCH CH2 H2O (2-hydroxyethyl formate) is a chemically significant ester that plays an important role in organic synthesis, industrial chemistry, and green energy applications. Its structure, combining both ester and hydroxyl functionalities, allows it to act as a versatile intermediate in many environmentally conscious processes. Understanding its properties and reactions not only enhances laboratory techniques but also supports the transition toward greener, more sustainable chemistry.
The specific intent is to inquire about the chemical reaction that occurs when 2-hydroxyethyl formate (HCOOCH CH2 H2O) is mixed with water (H2O). This reaction is hydrolysis, which breaks the ester down into:
- Formic Acid (HCOOH)
- Ethylene Glycol (CH2 H2O)
This knowledge is fundamental to understanding the chemical behavior and potential industrial applications of this specific ester-alcohol compound.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the full name of HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
It is known as 2-hydroxyethyl formate, an ester formed by reacting formic acid and ethylene glycol.
2. How is HCOOCH CH2 H2O prepared?
It is synthesized via the esterification of formic acid with ethylene glycol under acidic or catalytic conditions, producing water as a by-product.
3. Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O safe to handle?
Yes, it has low toxicity, but standard lab safety precautions—like gloves and goggles—are recommended.
4. What are the main uses of HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
It’s primarily used as a chemical intermediate, solvent, and model compound for studying ester reactions in organic chemistry.
5. Why is HCOOCH CH2 H2O important in green chemistry?
Because it’s biodegradable, recyclable, and derived from simple reactants, it supports eco-friendly research and industrial synthesis.
You May Also Like: Understanding the Importance of 2410381-07-4 CAS No in Modern Chemical Research